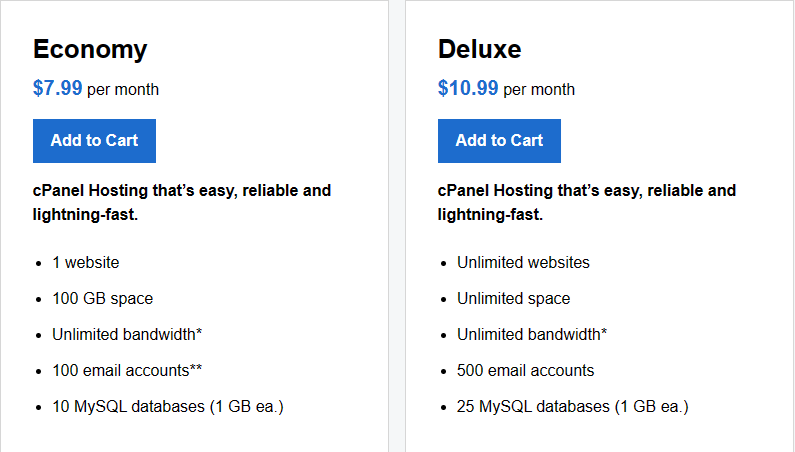
Shared web hosting is a type of hosting service where multiple websites share resources on the same server. In this hosting model, a single physical server hosts multiple accounts, each with its own domain name. These accounts share the server’s resources, including processing power, memory, and disk space.

Key features of shared web hosting include:
Cost-Effective: Shared hosting is generally more affordable compared to other hosting options, making it an attractive choice for individuals, small businesses, or those with budget constraints.
Ease of Use: Shared hosting is often designed to be user-friendly, making it suitable for beginners or those who don’t have extensive technical knowledge. The hosting provider typically manages server maintenance and security.
Shared Resources: Since multiple users share the same server, resources such as CPU, RAM, and storage are distributed among them. While this makes it cost-effective, it also means that the performance of one website can be affected by the activities of others on the same server.
Limited Control: Users on a shared hosting plan have limited control over server settings and configurations. The hosting provider handles most of the server management tasks.
Suitable for Small to Medium-sized Websites: Shared hosting is ideal for websites with moderate traffic, such as personal blogs, small business websites, or informational sites. It may not be suitable for high-traffic or resource-intensive websites.
Maintenance and Security: Server maintenance and security are typically managed by the hosting provider. This includes updates, patches, and ensuring the overall stability of the server.
Scalability: While shared hosting is a good starting point for new websites, it may become limiting as a site grows in terms of traffic and resource demands. In such cases, users may need to consider upgrading to a VPS (Virtual Private Server) or dedicated server hosting.
How Does Shared Web Hosting Work ?
Shared web hosting works by hosting multiple websites on a single physical server and sharing its resources among different users. Here’s an overview of how shared web hosting operates:
- Single Physical Server:
- In shared hosting, there is a single physical server that hosts multiple user accounts. Each user account represents a different website with its own domain name.
- Resource Sharing:
- Hosting Control Panel:
- Shared hosting providers typically offer a hosting control panel, such as cPanel or Plesk, which allows users to manage various aspects of their hosting account. This includes tasks such as creating email accounts, managing domains, and installing applications.
- Domain Association:
- Each user on the shared hosting server has their own domain name associated with their account. The hosting provider configures the server to recognize these domain names and directs incoming requests to the appropriate website files.
- File Storage:
- The website files for each user are stored on the server’s storage space. This includes HTML files, images, scripts, and other content that makes up the website.
- Server Software:
- Shared IP Address:
- In shared hosting, multiple websites may share the same IP address. This is because the server’s IP address is associated with the server itself, and each website on the server is identified by its domain name.
- Security Measures:
- Shared hosting providers implement security measures to isolate user accounts and prevent one user from accessing the files or data of another user. However, the shared nature of the environment introduces some level of risk, and security is a shared responsibility between the hosting provider and individual users.
- Traffic Distribution:
- Incoming web traffic is distributed among the hosted websites based on the domain name requested. The server processes these requests and serves the corresponding website’s content to the visitor’s web browser.
- Server Maintenance:
- Server maintenance tasks, including software updates, security patches, and hardware maintenance, are typically managed by the hosting provider. This helps ensure the stability and security of the shared hosting environment.
While shared hosting is a cost-effective and easy-to-use solution, it does have limitations in terms of resource allocation and customization. Websites with growing traffic or specific technical requirements may eventually need to consider other hosting options, such as Virtual Private Server (VPS) or dedicated server hosting.
The Advantages of Shared Web Hosting?
Shared web hosting offers several advantages, especially for individuals, small businesses, and those who are just starting with their online presence. Here are some key advantages of shared web hosting:
- Cost-Effective:
- Shared hosting is generally more affordable than other hosting options like VPS (Virtual Private Server) or dedicated hosting. It’s a budget-friendly option, making it accessible to individuals and small businesses with limited financial resources.
- Ease of Use:
- Shared hosting is designed to be user-friendly, making it suitable for beginners who may not have extensive technical knowledge. Hosting providers often offer intuitive control panels that simplify website management tasks.
- Quick Setup:
- Shared hosting plans are typically easy to set up, allowing users to get their websites online quickly. This is advantageous for individuals or businesses looking for a straightforward and fast solution.
- Managed Services:
- Resource Sharing:
- No Technical Maintenance:
- Shared hosting users don’t need to worry about the technical aspects of server maintenance, as these tasks are typically handled by the hosting provider. This includes hardware maintenance, software updates, and security configurations.
- Support Services:
- Shared hosting plans often come with customer support services provided by the hosting company. Users can rely on the hosting support team to assist with technical issues, troubleshooting, and general inquiries.
- Suitable for Small to Medium-Sized Websites:
- Shared hosting is well-suited for small to medium-sized websites with moderate traffic. It’s an excellent option for personal blogs, portfolio sites, informational websites, or small business sites.
- Scalability:
- While shared hosting may have limitations compared to more advanced hosting types, many providers offer the option to upgrade as a website grows. Users can start with a shared hosting plan and upgrade to a more robust solution as their needs evolve.
- Pre-Configured Environment:
- Shared hosting plans often come with pre-configured environments that are optimized for general website hosting. This simplicity is beneficial for users who want a hassle-free hosting experience.
Despite these advantages, it’s important to note that shared hosting may have limitations in terms of resource allocation and control compared to other hosting options. As a website grows, users may need to consider upgrading to a more advanced hosting solution.
The Disadvantages of Shared web Hosting?
While shared web hosting has its advantages, it also comes with certain disadvantages, especially as websites grow and their needs evolve. Here are some common drawbacks associated with shared hosting:
- Limited Resources:
- Performance Issues:
- Since resources are shared among multiple users, the overall performance of a website can be affected during periods of high traffic or resource demand. This can lead to slower loading times, especially if neighboring sites experience increased activity.
- Security Concerns:
- Limited Customization:
- Dependency on Server Configuration:
- Traffic Spikes Impact Performance:
- Shared hosting plans may struggle to handle sudden spikes in website traffic. If one site on the server experiences a surge in visitors, it can affect the performance of other sites sharing the resources.
- Risk of Overselling:
- Limited Control Over Server:
- Not Suitable for Resource-Intensive Applications:
- Shared hosting is not ideal for resource-intensive applications, such as large e-commerce sites or websites with extensive multimedia content. These types of websites may require more robust hosting solutions.
- Risk of Bad Neighbor Effect:
While shared hosting is a cost-effective solution for many users, those with growing websites or specific technical requirements may eventually need to consider more advanced hosting options, such as Virtual Private Server (VPS) hosting or dedicated server hosting, to address these limitations.