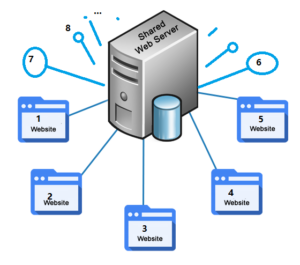
Web hosting is a service that allows organizations and individuals to post a website or web page on to the Internet. A web host, or web hosting service provider, is a business that provides the technologies and services needed for the website or webpage to be viewed in the Internet. Websites are hosted, or stored, on special computers called servers.
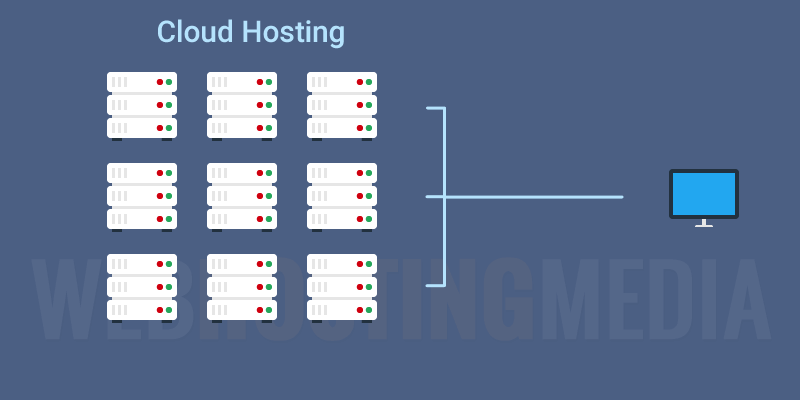
Web hosting services work by storing your website files in high-powered computers (web servers) connected to a very fast network. When someone types in your web address (such as www.powerhoster.com), the Internet connects to the web server holding your website files and then transfers your website information back to their computer. From there they can surf and view the pages of your website.
Anything related to managing these servers and its software, security, support, bandwidth, speed and so much more, is what we are all about! Because we provide web hosting services to over a million websites, we have special data centers that are built from the ground up to serve the purpose of web hosting.
When Internet users want to view your website, all they need to do is type your website address into their browser. Their computer will then connect to your server and your webpages will be delivered to them through the browser.
Most hosting companies require that you own your domain name in order to host with them. If you do not have a domain name, the hosting companies will help you purchase one.
Types of Web Hosting
As technology has progressed different types of web hosting have appeared to meet the different needs of websites and customers:
- Shared Web Hosting – you’re sharing the physical server environment with dozens to hundreds of other websites.
- Cloud Web Hosting – your website is hosted on multiple different servers simultaneously
- VPS Web Hosting – You have your own IP address, RAM and Hard-drive but share the server with other VPS account
- Dedicated Web Hosting – you have your own IPs and your own RAM, and Storage
- Reseller Web Hosting – You can sell your web hosting account to other customers
There are several types of web hosting, each designed to meet different needs and requirements. Here are some of the main types of web hosting:
- Shared Hosting:
- Multiple websites share resources on the same server. It’s a cost-effective option suitable for small to medium-sized websites with moderate traffic.
- Virtual Private Server (VPS) Hosting:
- Divides a physical server into multiple virtual servers, each with its own dedicated resources. It offers more control and scalability than shared hosting.
- Dedicated Server Hosting:
- Cloud Hosting:
- Utilizes a network of interconnected virtual and/or physical servers to host websites. It offers scalability and flexibility, allowing users to scale resources as needed.
- Managed WordPress Hosting:
- Specifically optimized for hosting WordPress websites. It often includes features like automatic updates, enhanced security, and specialized support for WordPress-related issues.
- Reseller Hosting:
- Allows individuals or companies to resell hosting services. Resellers purchase hosting resources and sell them to their clients, acting as hosting providers themselves.
- Colocation Hosting:
- Users own their servers but colocate them in a data center provided by a hosting provider. The provider offers power, cooling, and network infrastructure.
- Clustered Hosting:
- Involves hosting a website across multiple servers to improve performance, redundancy, and reliability. It distributes the load and enhances fault tolerance.
- Free Web Hosting:
- Provides hosting services at no cost, often with limitations on resources and features. It’s suitable for small personal projects or testing.
- E-commerce Hosting:
- Hosting solutions specifically designed for e-commerce platforms, providing features to support online stores. It often includes enhanced security and scalability.
- Green Hosting:
- Focuses on environmentally friendly practices, utilizing energy-efficient technologies and renewable energy sources to power data centers.
- Application Hosting:
- Tailored for hosting specific applications or platforms. Examples include Java hosting, Python hosting, or hosting for specific content management systems (CMS).
- Forum Hosting:
- Specialized hosting for online forums or discussion boards. It may include features specific to forum software and optimizations for handling user interactions.
Type of Web Hosting by Control Panel
Web hosting control panels provide users with an interface to manage various aspects of their hosting account, making it easier to configure and control their websites. Different hosting providers may offer different control panels. Here are some common types of web hosting control panels:
- cPanel:
- Description: cPanel is one of the most popular and widely used control panels. It provides a user-friendly interface for managing websites, domains, email accounts, databases, and more.
- Advantages: Intuitive interface, widespread usage, and extensive documentation.
- Plesk:
- Description: Plesk is a versatile control panel that supports both Windows and Linux hosting environments. It offers a range of features for managing websites, applications, and server settings.
- Advantages: Multi-platform support, user-friendly interface, and support for a variety of programming languages.
- DirectAdmin:
- Description: DirectAdmin is a lightweight and efficient control panel that simplifies the management of web hosting accounts. It is known for its simplicity and ease of use.
- Advantages: Lightweight, straightforward, and resource-efficient.
- ISPConfig:
- Description: ISPConfig is an open-source control panel that allows users to manage multiple servers from a single interface. It supports both Linux and Windows servers.
- Advantages: Open-source, customizable, and suitable for managing multiple servers.
- Webmin:
- Description: Webmin is an open-source control panel that provides a web-based interface for system administration on Unix-like systems. It is not specific to web hosting but offers server management capabilities.
- Advantages: Open-source, modular design, and extensibility.
- Ajenti:
- Description: Ajenti is a control panel that aims to be lightweight and resource-friendly. It provides a user-friendly interface for managing websites, databases, and server settings.
- Advantages: Lightweight, modern interface, and extensibility.
- VestaCP:
- Description: VestaCP is an open-source control panel designed to be simple and fast. It supports Apache and Nginx as web servers.
- Advantages: Open-source, lightweight, and easy to install.
- H-Sphere:
- Description: H-Sphere is a multi-server hosting automation solution that provides a centralized interface for managing websites, email, and other hosting-related services.
- Advantages: Scalable, supports multiple servers, and offers a range of features.
How does web hosting work
Web hosting happens when the files that make up a website are uploaded from a local computer on to a web server. The server’s resources, (RAM, hard drive space, and bandwidth) are allocated to the websites using it.
Your website is just a collection of different files. When you create a website you need a place to store all of these files. That place is your hosting company’s server.
On this server, you’ll store your website’s media, files, databases, and anything else required to properly render your website. Exactly how much storage you have will depend on the hosting plan you choose (more on this below).
If you’re just getting started online, then you’ll probably just be renting a portion of a server that you’re sharing with other websites. As your storage and traffic needs increase, then you may need to scale up to renting an entire physical server—or at least using the resources of one, with a cloud or VPS server.
When you sign up for a web hosting package you’ll usually get access to the server via a solution like cPanel. This makes it easy to upload your files to the server. Or, you can install a CMS like WordPress to easily build out your site.
In order to have a fully functioning website, you’ll also need to register a domain name. Once you purchase this you’ll point it towards your server, which lets the web browser know that this is where your files are located.
Then, when a person types in your domain name or clicks on a link to your site, the web browser gets the files from the server and displays them for the viewer. All of this should happen in a few seconds or less. If this process takes too long, then you either need to speed up your website or consider switching hosts entirely.
The division of server resources varies depending on the type of hosting plan chosen. To choose the appropriate hosting plan, you first need to differentiate between the plans available. This doesn’t have to be complicated. For the non-technical readers, let’s use a simple analogy: Choosing web hosting is similar to searching for office space:
How do you decide which type of office space is right for your needs? Is a workstation in an open co-working space enough, or the next best thing; an office within a business center. Do you have intentions to expand quickly or expect a lot of people coming and going? Would you consider renting an entire building or would building your own space appeal?
Aside from the style of office you use there are other considerations. How easy the rooms are to access, which functions they offer (extras such as a whiteboard, high-speed internet, and other facilities), and where are they located and the overall cost. These considerations will determine your needs and help decide which type of office is right for you. Let’s compare this selection process to deciding which web hosting fits.
- Shared hosting is similar to renting a workstation in a busy, noisy, open plan office or co-working space. You have all the modern conveniences: a desk, internet connection and some stationary and you share the space with other co-workers including the kitchen, printer, and restroom. You can’t do any makeovers to the space such as installing whiteboards etc. This is a popular option for launching small websites and not appropriate for large-scale commercial projects.
- A virtual private server (VPS) is a nice step up from shared hosting. Medium sized business will benefit from renting an office within a business park. With a VPS, users are isolated from each other. You have neighbors, but you are less dependant on them, and you can carry out any makeovers (customizations) as you like and organize your workstation on your own.
How to chose your web hosting provider?
Investigate their performance or claims in the following area:
- Uptime-Do they guarantee at least a 99% uptime? Where are their servers located?
- Years in the industry-One way to determine their credibility
- Customers-How many customers do they serve? In what locations do they have a presence?
- Online reviews and testimonials-These should give you a more factual idea of the company’s reputation
- Support-Does the company offer 24X7 support with trained personnel to assist you?
- Related products-Select a web hosting company that offers you other related web service products such as security, email and backup services. Getting it all in one place could reduce the time coordinating with different providers
- Security considerations
- Backup services
- Mobile Access– Can you access your control panel from a device on the go?